Hydrosalpinx: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management of Fallopian Tube Blockage
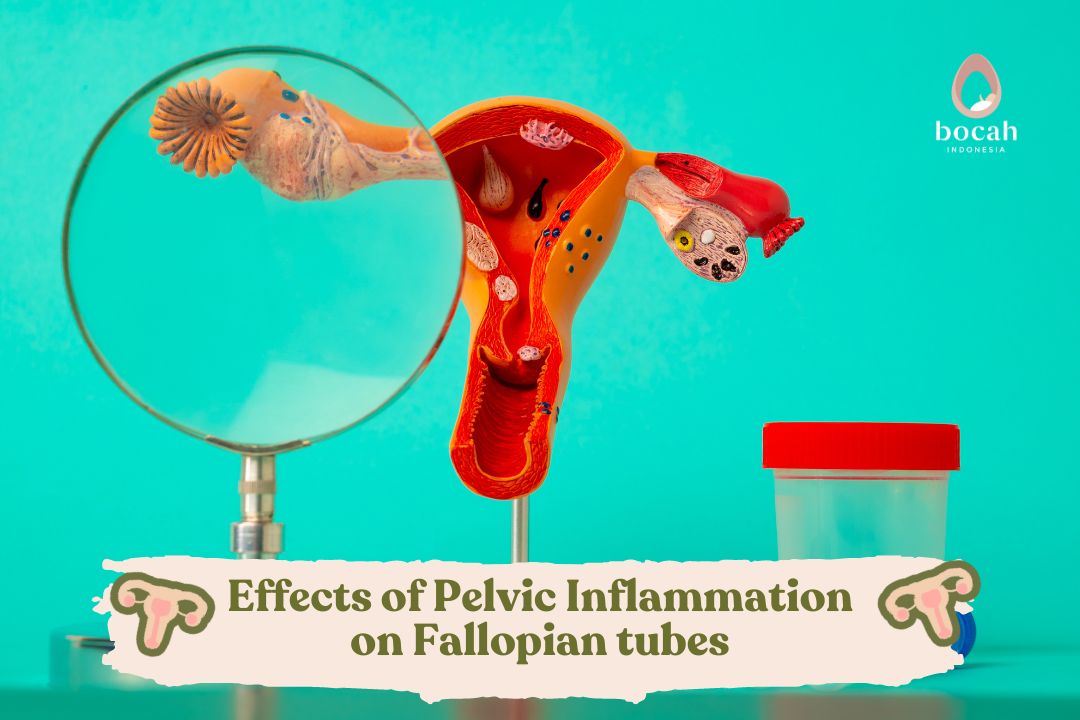
Hydrosalpinx is a cause of fallopian tube blockage. This condition can make it difficult for a woman to conceive. Many factors contribute to a woman’s difficulty in having a child, one of which is a problem with the fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes are reproductive organs connecting the ovaries to the uterus.
Each month, the ovaries produce a mature egg that travels toward the uterus through the fallopian tube, where the sperm and egg typically meet for fertilization. However, if the tube is blocked, the sperm’s journey to the egg is obstructed, making fertilization difficult. Hydrosalpinx is one specific cause of this tubal blockage, where any reproductive organ dysfunction can potentially lead to infertility, making pregnancy challenging.
What is Hydrosalpinx?
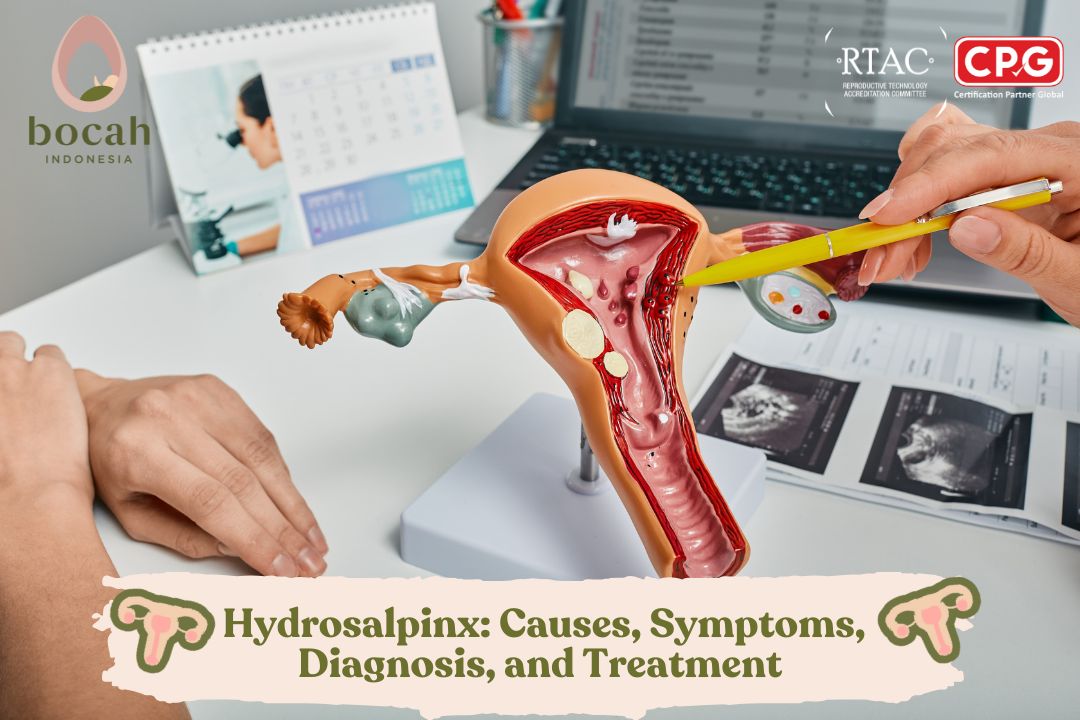
Hydrosalpinx is a condition involving the accumulation of fluid in one or both fallopian tubes, leading to a blockage. This fluid build-up is often linked to a history of prior infection.
What are the Causes of Hydrosalpinx?
Generally, hydrosalpinx is caused by bacterial infections that damage the fallopian tubes and cause inflammation. The primary infections leading to hydrosalpinx are Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. This inflammation frequently affects the area near the ovary (fimbriae). Inflamed fimbriae can close the tube, trapping fluid and causing swelling (distension). Other non-infectious causes include:
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining (endometrium) grows outside the uterus.
- A history of post-hysterectomy surgery.
- Severe adhesions (scar tissue/internal sticking) in the pelvic organs.
Hydrosalpinx hinders female fertility and complicates achieving pregnancy. Nevertheless, pregnancy remains possible if the hydrosalpinx is treated before embarking on a fertility program. A study in the Cureus Journal indicates that with the aid of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) and combined treatment, the pregnancy rate can increase up to 61%.
Mulai Journey of Hope
Symptoms of Hydrosalpinx
Hydrosalpinx is often asymptomatic (shows no symptoms). Many women are unaware of the condition until they undergo a fertility workup due to an inability to conceive. Tubal blockage may cause mild to severe pelvic pain and abnormal vaginal discharge. Furthermore, tubal blockage can lead to complications such as a painful ectopic pregnancy if the condition is not addressed promptly. Sometimes, women dismiss lower abdominal or pelvic pain as normal menstrual discomfort, but if accompanied by unusual discharge, it may signal hydrosalpinx.
How is Hydrosalpinx Diagnosed?
Hydrosalpinx cannot be determined without a proper examination and diagnosis. Key methods used for diagnosis include:
- Ultrasonography (USG): Specifically, a Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS) is used. The probe is inserted through the vagina to view the reproductive organs more clearly and in detail, helping detect the characteristic fluid-filled, sausage-shaped tubes.
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): This is a common procedure to diagnose tubal obstruction. Contrast dye is injected into the uterus, and its movement is monitored via X-ray. If the fluid flows out of the tubes into the pelvic cavity, the tubes are open. If the contrast stops flowing, an obstruction is present.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure where a doctor makes a small incision in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope (camera) to visually inspect the pelvic cavity and confirm the presence of blockages or adhesions.
How is Hydrosalpinx Managed?
Untreated hydrosalpinx can lead to difficulty conceiving and an increased risk of complications. Therefore, treatment is crucial to resolve the blockage. There are two primary surgical procedures for managing hydrosalpinx:
- Salpingostomy: A procedure for fallopian tube repair often performed via laparoscopy for mild cases. The blocked tube is incised to drain the fluid and potentially reopen the distal end of the tube.
- Salpingectomy: The procedure to surgically remove one or both blocked tubes. This is performed under anesthesia using laparoscopy, resulting in minimal surgical scarring.
Addressing hydrosalpinx significantly raises the chance of a successful pregnancy.
Source:
- El-Kharoubi, A.F. (2023). Tubal Pathologies and Fertility Outcomes: A Review. Cureus. 2023 May; 15(5): e38881.
- Ng, K.Y.B., Cheong, Y. (2019). Hydrosalpinx – Salpingostomy, salpingectomy or tubal occlusion. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2019 Aug: 59:41-47.
- Honore, G.M., et al. (1999). Pathophysiology and management of proximal tubal blockage. Pathophysiology and management of proximal tubal blockage. Fertil Steril. 1999; 71: 785-795.
- Fasting While Trying to Conceive? Healthy Meal Ideas for the Entire Month - 04/03/2026
- 12 Foods to Help You Get Pregnant Faster - 03/03/2026
- 3 Juice Recipes for a Pregnancy Program - 26/02/2026