The Difference Between Egg Freezing and Embryo Freezing

In recent decades, the journey to parenthood has experienced remarkable progress through assisted reproductive technologies. Among them, the freezing of eggs and embryos has revolutionized family planning for individuals and couples struggling with infertility, as well as those who wish to delay pregnancy for career or personal reasons.
Comparing Egg Freezing and Embryo Freezing
Egg freezing (oocyte cryopreservation) and embryo freezing may sound similar. However, in reality, the two procedures are significantly different.
The Process: Egg Freezing vs. Embryo Freezing
Egg freezing, or medically known as oocyte cryopreservation, begins with a consultation with a fertility specialist and laboratory testing. After evaluation, the woman undergoes ovarian stimulation with hormonal medications, along with regular monitoring and ultrasound examinations to assess follicle development.
Once the eggs are mature, they are collected through an ovum pick-up procedure and frozen for future use. When the woman is ready to conceive, the frozen eggs are thawed and fertilized with sperm in the laboratory. The resulting embryo is then transferred into the uterus to implant.
Egg freezing is particularly beneficial for women concerned about the natural decline of their ovarian reserve with age, or those undergoing medical treatments that may affect fertility.
Tanya Mincah tentang Promil?
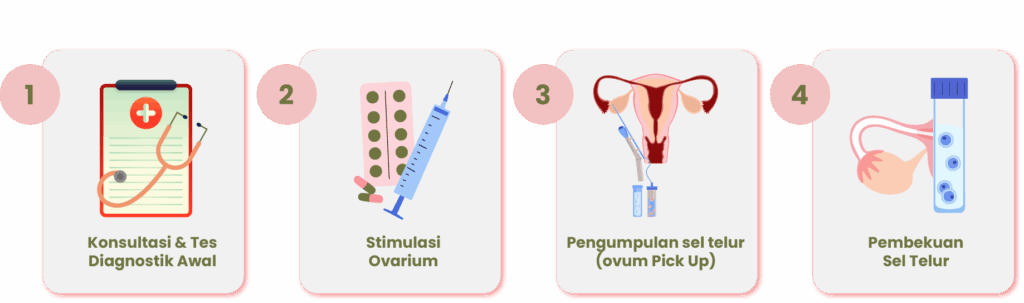
Figure 1. The process of egg freezing.
In embryo freezing, the initial steps are the same as egg freezing up to the point of egg retrieval. However, the eggs are fertilized with sperm in the laboratory to form embryos, which are then frozen for later use. Embryo freezing is commonly performed in couples who are ready to become parents and are undergoing IVF treatment, where multiple embryos may be created.
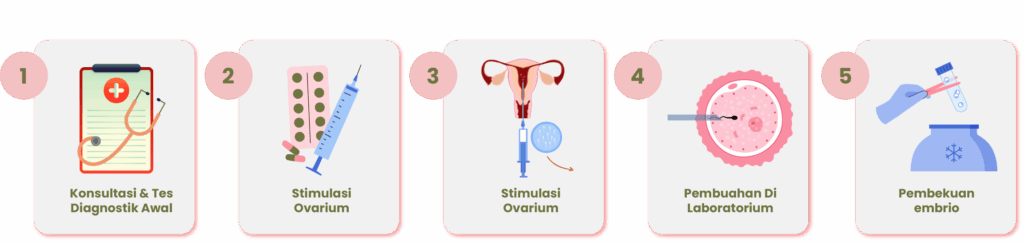
Figure 2. The process of embryo freezing.
Advantages of Each Procedure
One of the greatest benefits of egg freezing is that it does not require sperm. This makes it an ideal option for single women, those considering donor sperm, or women uncertain about their current partner. Egg freezing allows women to preserve their fertility independently and maintain autonomy over future reproductive choices.
On the other hand, embryo freezing offers unique advantages. Through fertilization and embryo culture, the number of viable embryos available for transfer can be determined. This differs from egg freezing, where the outcome remains uncertain, often requiring more eggs to be collected and stored.
Additionally, embryo freezing has a slightly higher survival rate than egg freezing (95% vs. 90%). Embryos can also be stored longer due to their cellular structure. Since an egg is a single cell, it is more fragile during the freezing process, as water is removed and the egg is stored in liquid nitrogen. By contrast, embryos are made up of hundreds of cells; even when water is removed, their multi-cell structure makes them more resilient.
Another advantage of embryo freezing is the option for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT), offering higher success rates for couples undergoing IVF.
Summary of Benefits: Egg Freezing vs. Embryo Freezing
Egg Freezing
-
Can be performed at any reproductive age
-
Does not require fertilization, allowing women to proceed independently without a partner
-
Preserves fertility in women with certain medical conditions
-
Less ethical controversy compared to embryo freezing
Embryo Freezing
-
Reduces the need for repeated egg retrieval cycles
-
Embryos have higher survival rates during freezing and thawing
-
Higher success rates for achieving pregnancy compared to egg freezing
-
Allows for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT)
Drawbacks
Both egg and embryo freezing carry the risk of cell loss during thawing. However, since eggs are more fragile, a woman may lose more eggs than expected when thawing. Typically, around 15 or more frozen eggs are required to achieve embryo formation, due to the risks of cell loss during thawing, fertilization, and embryo transfer. Therefore, more eggs are usually needed in egg freezing compared to embryo freezing, making the process more frequent and complex.
Embryo freezing, on the other hand, comes with ethical dilemmas. In many belief systems, embryos are considered life. This raises moral challenges when discarding unused embryos, leaving some couples feeling obligated to use all of them—potentially leading to more children than originally planned.
Drawbacks of Egg Freezing
-
Lower success rates compared to embryo freezing
-
High costs, depending on the clinic, number of eggs frozen, storage duration, and frequency of retrieval cycles
Drawbacks of Embryo Freezing
-
Ethical concerns about unused embryos
-
Requires sperm/partner involvement
-
More expensive per cycle compared to egg freezing
Which Is Better and More Successful?
The answer depends on several factors, including the quality of eggs and embryos. A major limitation of egg freezing is the inability to assess egg quality beforehand. An egg’s potential is only revealed once it is fertilized and develops into an embryo. By contrast, embryos undergo multiple checkpoints, providing a clearer picture of their viability and potential to develop into a healthy baby.
Generally, embryos have higher survival rates during freezing and thawing than eggs. Advances in vitrification and embryo freezing techniques have further improved success rates. However, outcomes still vary widely depending on factors such as a woman’s age at the time of freezing, egg/embryo quality, and the expertise of the fertility clinic.
Success Rates
-
Egg freezing: Success rates have improved significantly in recent years, particularly when eggs are frozen at a younger age. Studies show that women under 35 who freeze their eggs have a 60–80% chance of eventual pregnancy, with live birth rates of around 25%.
-
Embryo freezing: Offers higher success rates due to embryo selection and PGT. Live birth rates per frozen embryo transfer are typically between 40–60%.
Which Option Should You Choose?
Both methods provide opportunities to preserve fertility and extend reproductive timelines. Deciding between the two is not easy and requires considering several factors:
-
Relationship status and future plans
-
If you are in a committed relationship and planning to have children with your current partner, embryo freezing may be more suitable.
-
If you are single or unsure about your partner, egg freezing offers more independence and flexibility.
-
-
Age
-
Younger women generally have healthier, more viable eggs. Freezing eggs in the 20s or early 30s increases the likelihood of success.
-
For women in their late 30s or older who have a partner, embryo freezing is often the better option.
-
-
Medical conditions
-
Women diagnosed with cancer or autoimmune diseases may consider egg freezing before undergoing treatments that could harm fertility.
-
Women with conditions such as endometriosis may also benefit from egg freezing.
-
Couples with genetic risks may prefer embryo freezing with PGT to select embryos free from genetic abnormalities.
-
-
Ethical, emotional, and psychological considerations
-
Embryo freezing may raise ethical concerns, as some couples struggle with the idea of discarding unused embryos.
-
Egg freezing avoids this issue, since only eggs—not embryos—are stored.
-
-
Financial considerations and success rates
-
Both procedures can be costly, with prices varying depending on clinic and location.
-
Egg freezing is generally less expensive, since it does not involve fertilization or embryo culture.
-
If financially feasible and medically appropriate, some couples may choose to undergo both: one cycle to freeze eggs and another to freeze embryos.
-
Conclusion
Both egg freezing and embryo freezing provide extraordinary opportunities for family planning, giving individuals and couples greater control over their reproductive future. Choosing between the two, however, is a complex decision that requires careful consideration of medical, personal, ethical, and financial factors. Ultimately, this is a highly personal choice that should be made in consultation with a qualified fertility specialist.
Source:
- Cascante SD, Berkeley AS, Licciardi F, McCaffrey C, Grifo JA. Planned oocyte cryopreservation: the state of the ART. Reproductive BioMedicine Online. 2023 Aug 24:103367.
- Casciani V, Monseur B, Cimadomo D, Alvero R, Rienzi L. Oocyte and embryo cryopreservation in assisted reproductive technology: past achievements and current challenges. Fertility and sterility. 2023 Sep 1;120(3):506-20.
- Konc J, Kanyó K, Kriston R, Somoskői B, Cseh S. Cryopreservation of embryos and oocytes in human assisted reproduction. BioMed research international. 2014;2014(1):307268.
- Mesen TB, Mersereau JE, Kane JB, Steiner AZ. Optimal timing for elective egg freezing. Fertility and sterility. 2015 Jun 1;103(6):1551-6.
- Pai HD, Baid R, Palshetkar NP, Pai A, Pai RD, Palshetkar R. Oocyte cryopreservation-current scenario and future perspectives: a narrative review. Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences. 2021 Oct 1;14(4):340-9.
- Polyakov A, Piskopos J, Rozen G. Focus: Elective egg freezing: State of the ART. Australian Journal of General Practice. 2023 Jan 1;52(1/2):20-3.