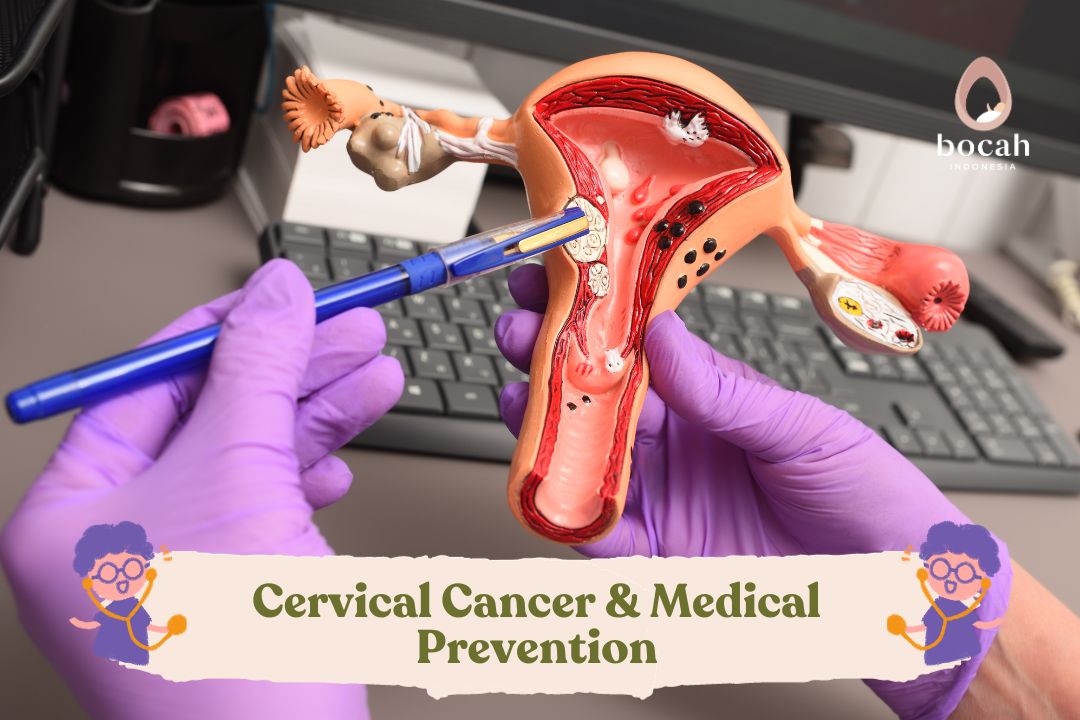
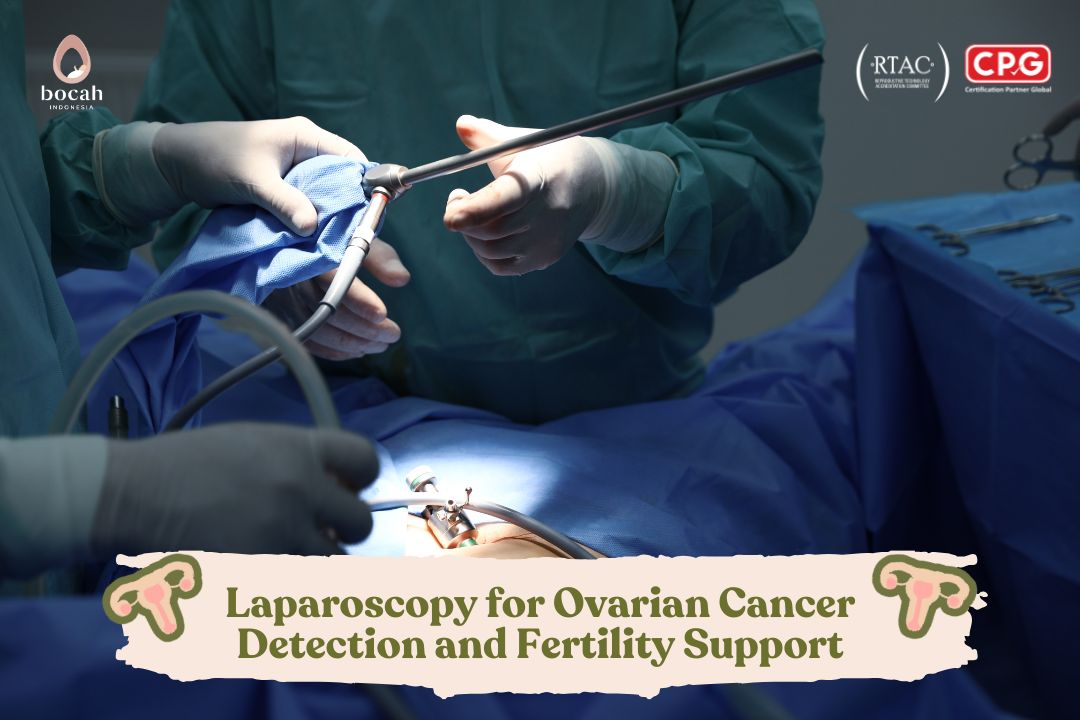
Laparoscopy for Ovarian Cancer Detection and Fertility Support
For many women, maintaining reproductive health also means preserving the opportunity to become a mother. However, conditions such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or even ovarian cancer can interfere with the reproductive system and make conception more difficult.
One of the most widely used modern medical technologies to assist in both diagnosis and treatment of these conditions is laparoscopy—also known as keyhole surgery.
This procedure allows doctors to visualize internal organs without making large incisions, using only a small cut approximately 0.5–1.5 cm in size.
Today, laparoscopy has become the preferred choice in many fertility and oncology clinics, including Bocah Indonesia, due to its minimal pain, rapid recovery, and high diagnostic accuracy.
What Is Laparoscopy and How Is It Performed?
Laparoscopy uses a specialized instrument called a laparoscope, a small tube equipped with a camera and light source at its tip.
The camera transmits real-time images to a high-resolution monitor, allowing doctors to see the internal organs within the abdominal and pelvic cavities in detail.
Procedure Steps
-
Administration of Anesthesia (General Anesthesia) – The patient is fully sedated and feels no pain during the procedure.
Mulai Journey of Hope
-
Micro-Incision – A small incision is made near the navel to insert the laparoscope.
-
CO₂ Insufflation – Carbon dioxide gas is used to gently inflate the abdomen, creating space for visualization.
-
Organ Visualization – The camera provides a detailed view of organs such as the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding tissues.
-
Medical Intervention – If abnormalities are detected, the doctor may perform a biopsy, remove a cyst, or excise endometriotic tissue.
The procedure usually lasts 30–90 minutes, depending on its complexity. Afterward, most patients can return home the same day or after one night of observation.
Laparoscopy in the Detection and Management of Ovarian Cancer
1. Diagnosis and Biopsy
Ovarian cancer is often difficult to detect early because its symptoms mimic common digestive or abdominal complaints such as bloating or pain.
Through laparoscopy, doctors can directly inspect the ovaries and nearby tissues.
If a suspicious mass is found, a biopsy (tissue sampling) can be performed for pathological examination in the laboratory.
2. Cancer Staging
Laparoscopy helps determine how far the cancer has spread to surrounding organs such as the uterus, omentum, or intestines.
This information is crucial in planning the next treatment steps—whether additional surgery or chemotherapy should be performed first.
3. Evaluation of Treatment Response
In some cases, laparoscopy is also used to monitor the response to chemotherapy and confirm whether cancerous tissue has decreased or been completely removed.
4. Clinical Advantages
-
Smaller incision → minimal pain.
-
Quick recovery (average 3–5 days).
-
Lower infection risk.
-
Better cosmetic outcomes (tiny scars).
-
Clearer visualization of tissues than with ultrasound or CT scan.
The Role of Laparoscopy in Fertility and Pregnancy Programs
Beyond oncology, laparoscopy also plays a significant role in fertility programs, particularly for women with reproductive system disorders.
1. Treating Endometriosis
Endometriosis—the growth of tissue similar to the uterine lining outside the uterus—can cause severe pain and interfere with ovulation.
Through laparoscopy, doctors can remove endometriotic tissue without damaging reproductive organs, thereby improving the chances of conception.
2. Removing Ovarian Cysts
Large or suspicious ovarian cysts often disrupt egg maturation.
Laparoscopy allows precise cyst removal while preserving healthy ovarian tissue and maintaining normal ovarian function.
3. Opening Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Blockage of the fallopian tubes is a common cause of infertility.
Laparoscopy enables doctors to clear these blockages, allowing eggs and sperm to meet naturally once again.
4. Assessing Reproductive Organ Quality
During laparoscopy, doctors can directly assess the condition of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
This valuable information helps determine the next fertility strategy, whether through natural conception, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Advantages Compared to Open Surgery
| Aspect | Laparoscopy | Conventional Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Incision Size | 0.5–1.5 cm | 10–20 cm |
| Postoperative Pain | Mild | Severe |
| Hospital Stay | 1–2 days | 5–10 days |
| Infection Risk | Low | High |
| Scar Appearance | Minimal | Large |
| Recovery Time | 5 days | >2 weeks |
Additional Benefits:
-
Faster recovery, enabling patients to begin chemotherapy or fertility treatment sooner.
-
Reduced risk of bleeding and adhesions.
-
Superior visualization for precise diagnosis and treatment.
Risks and Side Effects
Although laparoscopy is generally safe, potential risks include:
-
Mild: nausea, shoulder discomfort due to CO₂ gas, mild incision pain.
-
Serious (rare): heavy bleeding, infection, injury to internal organs (such as bowel or bladder), or allergic reaction to anesthesia.
These risks can be minimized when the procedure is performed by an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist (Sp.OG-KFER) in a sterile, well-equipped surgical environment.
Post-Laparoscopy Care
Recovery is typically quick, and most patients can walk within a few hours.
Postoperative care tips:
-
Avoid strenuous activity for 3–5 days.
-
Eat a nutritious diet to promote tissue healing.
-
Drink plenty of water to help the body absorb residual CO₂ gas.
-
Attend follow-up appointments for wound evaluation and biopsy results.
Laparoscopy at Bocah Indonesia
At Bocah Indonesia Fertility Clinic, laparoscopy is performed by a team of experienced fertility and reproductive endocrinology specialists (Sp.OG-KFER) using modern high-definition surgical cameras.
Each patient receives:
-
Comprehensive preoperative evaluation, including ultrasound and tumor marker (CA-125) testing.
-
Surgery in a sterile, hospital-grade operating room.
-
Postoperative medical monitoring and personalized recovery guidance.
If laparoscopy reveals conditions such as endometriosis, cysts, or pelvic adhesions that affect fertility, Bocah Indonesia’s medical team will design a personalized fertility plan, which may include:
-
Ovulation stimulation,
-
Intrauterine insemination (IUI), or
-
In vitro fertilization (IVF).
This holistic and patient-centered approach helps women safely and effectively move forward on their journey to pregnancy.
Conclusion
Laparoscopy offers a modern, minimally invasive, and safe solution for:
-
Diagnosing and managing ovarian cancer,
-
Treating fertility-related issues such as endometriosis and ovarian cysts, and
-
Supporting more effective and targeted pregnancy programs.
With advanced technology and experienced specialists at Bocah Indonesia, women can receive faster, more comfortable, and comprehensive reproductive care.
Source:
-
Frontiers in Oncology. (2022). Role of Laparoscopy in Gynecologic Cancer Management.
-
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology. (2023). Diagnostic Accuracy and Morbidity of Laparoscopic Staging in Ovarian Cancer.
-
National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2024). Minimally Invasive Surgery for Ovarian Malignancy.
-
Kementerian Kesehatan RI – Pedoman Penanganan Kanker Ovarium.
-
Tim Medis Bocah Indonesia – Panduan Laparoskopi dan Fertilitas Wanita 2025.