Egg and Sperm Quality: The Key to Pregnancy Success for Couples

The quality of both egg and sperm significantly determines the success rate of pregnancy programs. Factors such as age, lifestyle, nutrition, and medical conditions all play important roles in fertility. Medical evaluations and adopting a healthy lifestyle are essential steps.
Deciding to start a pregnancy program (promil) is a significant commitment that requires readiness from both partners. One of the key factors for promil success is ensuring that both egg and sperm are in optimal condition.
The health of eggs and sperm is influenced by various factors, including lifestyle, nutrition, and overall health status. Therefore, it is crucial for both partners to undergo fertility examinations at the start of their journey. Let’s explore how egg and sperm quality can be evaluated.
Factors That Affect Egg Quality in Women
The egg (ovum) is the female reproductive cell produced by the ovaries. Each month, one egg is released and becomes ready for fertilization. However, egg quality may be influenced by several factors:
1. Age
Age is a major determinant of egg quality. As women grow older, both the quantity and quality of eggs decrease. Women in their 20s generally have higher-quality eggs, while after age 35, egg quality tends to decline significantly. This impacts not only the chances of conception but also increases the risk of miscarriage.
Tanya Mincah tentang Promil?
2. Lifestyle and Environment
Unhealthy habits such as poor diet, smoking, alcohol consumption, and environmental pollution can damage egg quality. A nutritious diet rich in folic acid, vitamin C, and antioxidants, along with regular exercise and stress management, can help improve egg health.
3. Medical Conditions
Certain medical issues such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, or other hormonal disorders may affect egg quality. Women with these conditions are encouraged to consult a physician for proper treatment.
Signs of Poor Egg Quality
Some indicators may suggest suboptimal egg quality, which may make conception more difficult:
-
Irregular menstrual cycles: May signal ovulation disorders, reducing mature egg release.
-
Advanced maternal age: After age 35, egg quality naturally declines, affecting fertilization potential.
-
History of recurrent miscarriage: May indicate chromosomal abnormalities in the egg.
-
Abnormal hormone levels: Low AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) or high FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) can suggest diminished ovarian reserve.
Through comprehensive fertility testing, women can better understand their reproductive health and receive tailored medical advice.
Factors That Affect Sperm Quality in Men
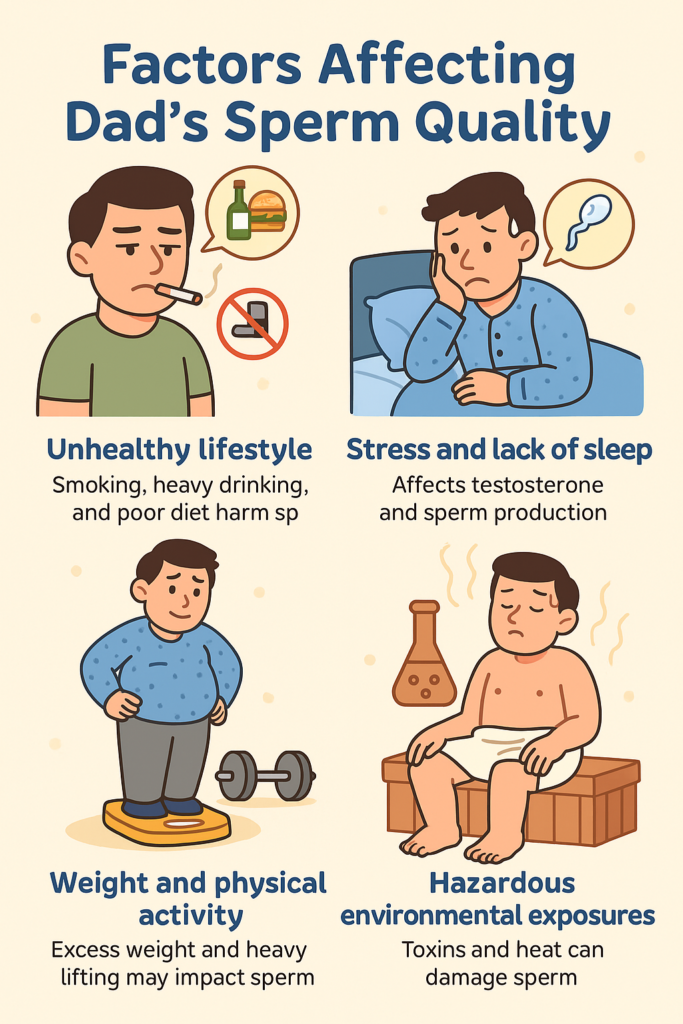
Sperm is the male reproductive cell responsible for fertilizing the egg. Sperm quality greatly impacts fertilization success and is influenced by lifestyle, age, and overall physical health.
1. Unhealthy Lifestyle
-
Smoking can damage sperm DNA and reduce count and motility.
-
Excessive alcohol disrupts testosterone levels, which affects sperm production.
-
Poor nutrition, particularly deficiencies in zinc, vitamin C, vitamin D, and folic acid, can significantly impair sperm health.
Shifting to a healthier lifestyle is strongly advised for men aiming to improve fertility.
2. Chronic Stress and Sleep Deprivation
-
Prolonged stress alters reproductive hormones, including testosterone, and can suppress sperm production.
-
Poor sleep reduces the body’s ability to regenerate sperm cells.
-
Managing stress and maintaining healthy sleep patterns are vital for reproductive health.
3. Body Weight and Physical Activity
-
Both obesity and being underweight can disrupt hormone levels and sperm production.
-
Excessive physical activity, especially heavy weightlifting, may elevate scrotal temperature, damaging sperm.
-
Balanced physical activity helps maintain healthy sperm production.
4. Environmental Toxins
-
Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, industrial solvents, and prolonged heat (e.g., hot tubs, saunas, prolonged sitting) can impair sperm quality.
-
Reducing exposure to these risk factors is important for sperm health.
Signs of Poor Sperm Quality
Some common signs may indicate suboptimal sperm quality:
-
Low sperm concentration: Normal count is >15 million sperm per ml; lower levels reduce fertilization chances.
-
Poor motility: Fewer than 40% motile sperm struggle to reach the egg.
-
Abnormal morphology: Misshapen heads or defective tails limit the ability to fertilize.
-
Abnormal semen volume: Less than 1.5 ml or excessive volume may signal glandular dysfunction.
-
Unusual color/texture: Yellowish, grayish, watery, or thick consistency may indicate infection or abnormalities.
-
Ejaculatory difficulties: Conditions such as retrograde ejaculation prevent sperm from reaching the uterus.
Consulting a fertility specialist can help men address these issues and optimize their fertility for pregnancy success.
Egg and Sperm Quality in Fertility Programs
Both egg and sperm quality are closely linked to pregnancy outcomes. For couples planning to conceive, reproductive health must be a shared responsibility. Here are key steps to enhance fertility:
1. Healthy Nutrition
-
Women should consume a balanced diet rich in folic acid for egg health.
-
Men should prioritize foods high in zinc and vitamin C to improve sperm quality.
2. Avoid Harmful Habits
-
Avoid smoking, excessive alcohol, and high caffeine intake, which can impair reproductive cells.
3. Regular Exercise
-
Exercise promotes better blood circulation, maintains ideal body weight, and reduces stress—all contributing to reproductive health.
4. Consult a Doctor
-
Fertility assessments and medical consultations are essential. In certain cases, doctors may recommend additional treatments, such as artificial insemination or IVF (In Vitro Fertilization).
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining balanced nutrition, and eliminating bad habits, couples can significantly improve their chances of conceiving. If concerns arise about egg or sperm quality, always seek guidance from a fertility specialist for the most appropriate care.
Source:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020). Planning for Pregnancy.
- Mayo Clinic (2019). Getting Pregnant.
- NHS UK (2020). Infertility.
- Stöppler, M.C., MedicineNet (2019). Pregnancy Planning Tips, Foods and Infections to Avoid, and How to Prepare for the Baby.
- Gelman, L., Parents. Get Pregnant Faster: Your 7-Step Plan.
- WebMD (2020). Getting Started on Getting Pregnant.