Uterine Corpus Cancer Causes Mother’s Pelvic Pain
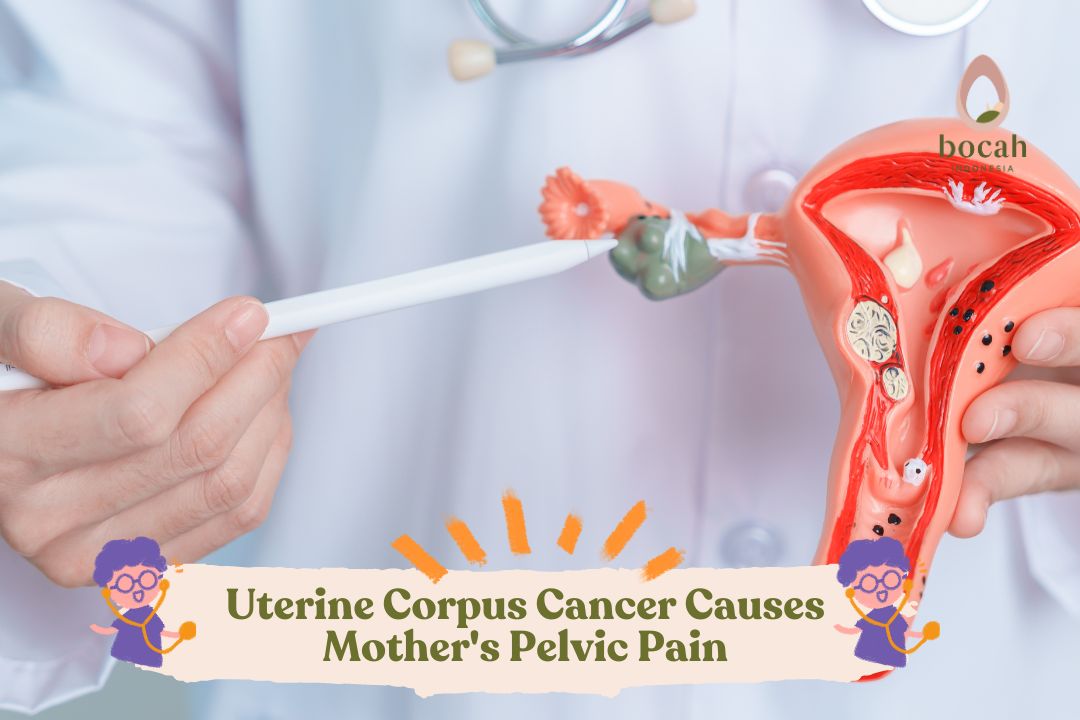
Uterine corpus cancer can cause pelvic pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse for mothers.
Uterine corpus cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, is a common type of gynecological cancer in women. Recognizing symptoms, risk factors, and taking appropriate prevention measures can help reduce the risk of uterine corpus cancer.
Although the overall prognosis is relatively good, high-grade endometrial cancer carries a risk of recurrence. This makes prevention of endometrial cancer recurrence extremely important.
What is Uterine Corpus?
The uterine corpus, or one of the main parts of the uterus, is a muscular and hollow organ that is part of the mother’s reproductive system. This organ plays a major role in providing an environment that supports embryo development and pregnancy. Here are some key aspects of the uterine corpus:
-
Anatomy and Structure
The uterine corpus is located in the lower part of the pelvic cavity and has a pear-like shape. It consists of two main parts, namely the cervix (the neck of the uterus) which connects to the vagina, and the corpus (the body of the uterus) which extends upward from the cervix.
Mulai Journey of Hope
The uterine wall consists of several layers, including the endometrium (inner layer that undergoes changes during the menstrual cycle), the myometrium (middle muscular layer responsible for contractions), and the perimetrium (outer layer that lines the uterus).
-
Role in Menstrual Cycle
The uterine corpus plays a crucial role in a woman’s menstrual cycle. Each cycle, the endometrium undergoes growth and preparation as a site for fertilized embryos. If fertilization does not occur, the endometrium is shed in the form of menstruation.
-
Implantation Process
The uterine corpus serves as the site for the implantation process of fertilized embryos. After fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube, the embryo reaches the uterus and embeds itself into the endometrium to begin its development.
-
Maintaining Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the uterine corpus functions to support and nurture the developing fetus. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone are produced to maintain pregnancy and prevent menstruation.
In the early trimester of pregnancy, the uterine corpus prepares the endometrium and maintains pregnancy stability. In the second and third trimesters, the uterine corpus plays a role in sustaining the developing fetus.
The uterine corpus plays a vital role in the journey of pregnancy and mother’s fertility. A deep understanding of the physiology and function of this organ is important to support crucial phases in mother’s pregnancy.
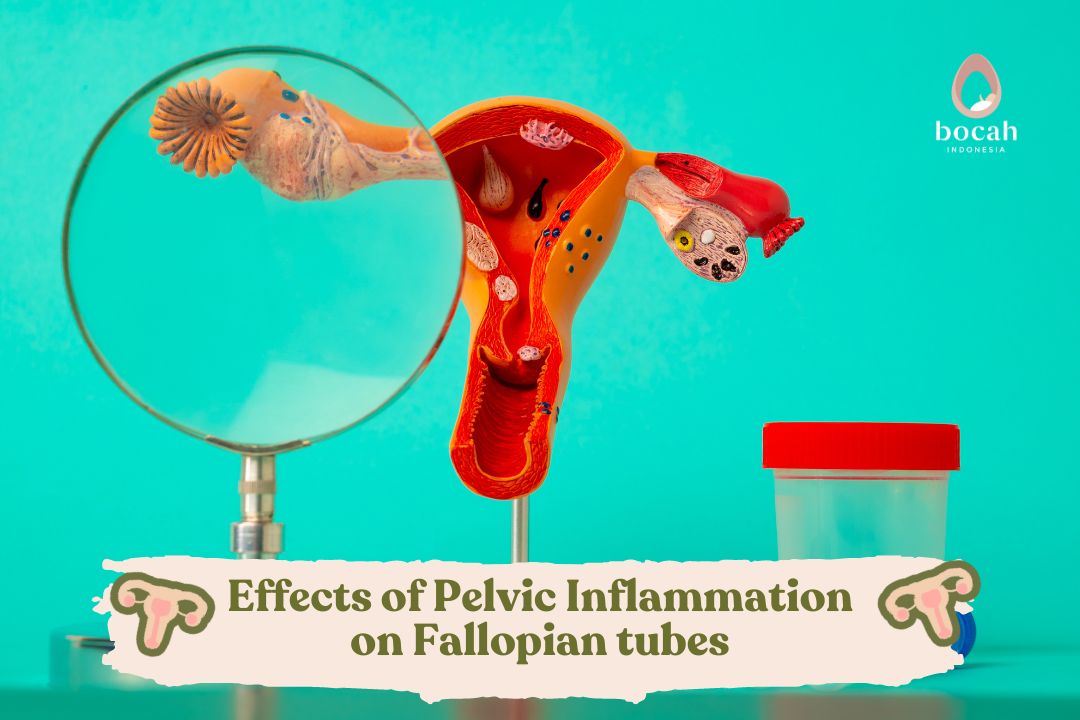
Symptoms and Risk Factors of Uterine Corpus Cancer
The signs and symptoms of uterine corpus cancer vary depending on the stage of the disease. Some symptoms of uterine corpus cancer that mothers may experience include:
-
Abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding between menstrual periods or bleeding after menopause.
-
Pelvic pain.
-
Pain during sexual intercourse.
-
Unexplained weight loss.
-
Swelling in the pelvic or abdominal area.
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of mothers developing uterine corpus cancer, including:
-
Age, the risk of uterine corpus cancer increases with age.
-
Obesity can increase estrogen hormone levels, which can increase the risk of uterine corpus cancer.
-
Family history, if there are family members who have had uterine corpus cancer, the risk for mothers to experience it also increases.
-
History of endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial hyperplasia is a condition where the uterine lining grows excessively, which can increase the risk of uterine corpus cancer.
-
History of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), mothers with a history of polycystic ovary syndrome have a higher risk of developing uterine corpus cancer.
Diagnosis for Uterine Corpus Management
To diagnose uterine corpus cancer, doctors may perform several tests and procedures for mothers to undergo, including:
-
Physical examination, doctors will perform a physical examination to look for signs of uterine corpus cancer, such as lumps or changes in the uterus.
-
Pap smear test, This test is done to check for abnormal cells in the cervix.
-
Biopsy, doctors will take tissue samples from the uterus to examine under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer.
-
Pelvic ultrasound can help doctors see a clearer picture of the uterus and other pelvic organs.
Treatment and Prevention for Uterine Corpus Cancer
Treatment for uterine corpus cancer depends on the stage of the disease, risk factors, and individual patient needs. There are several treatments commonly performed by doctors to address uterine corpus, including:
-
Hysterectomy, this procedure involves the removal of the uterus and cervix. Hysterectomy is often the primary treatment method for uterine corpus cancer.
-
Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, this procedure involves the removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes.
-
Lymphadenectomy, this procedure is performed to remove lymph nodes around the uterus. Lymphadenectomy can help determine if the cancer has spread to lymph nodes.
-
Radiation therapy with high-energy beams can destroy uterine corpus cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be done before or after surgery to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
-
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be done before or after surgery, depending on the patient’s needs.
There are several steps mothers can take to prevent uterine corpus cancer, including:
-
Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of uterine corpus cancer.
-
Regular exercise can help maintain health and reduce the risk of uterine corpus cancer.
-
Choosing healthy, fiber-rich foods can help maintain uterine health.
-
Avoiding postmenopausal hormone therapy, postmenopausal hormone therapy can increase the risk of uterine corpus cancer.
-
Undergoing regular check-ups and Pap smear tests can help detect uterine corpus cancer at an early stage.
Those are the explanations about uterine corpus cancer that mothers need to be aware of. If mothers are looking for ways to conceive quickly and want to join a pregnancy program, read more information on the Bocah Indonesia website.
This article has been medically reviewed by Dr. Chitra Fatimah.
Source:
- Amant F, et al. (2018). Cancer of the corpus uteri.Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 143(Suppl 2), 37-50. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.12612. https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ijgo.12612
- Koskas M, et al. (2021). Cancer of the corpus uteri: 2021 update. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 155(Suppl 1), 45-60. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.13866. https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ijgo.13866
- Iwase H, et al. (2018). The Clinical Features of Recurrent Endometrial Cancer in Japan: Chemotherapy Instead of Radiotherapy as Postoperative Adjuvant Treatment. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 28(8), 1616-1623. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000001346. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30095709/
- Fasting While Trying to Conceive? Healthy Meal Ideas for the Entire Month - 04/03/2026
- 12 Foods to Help You Get Pregnant Faster - 03/03/2026
- 3 Juice Recipes for a Pregnancy Program - 26/02/2026