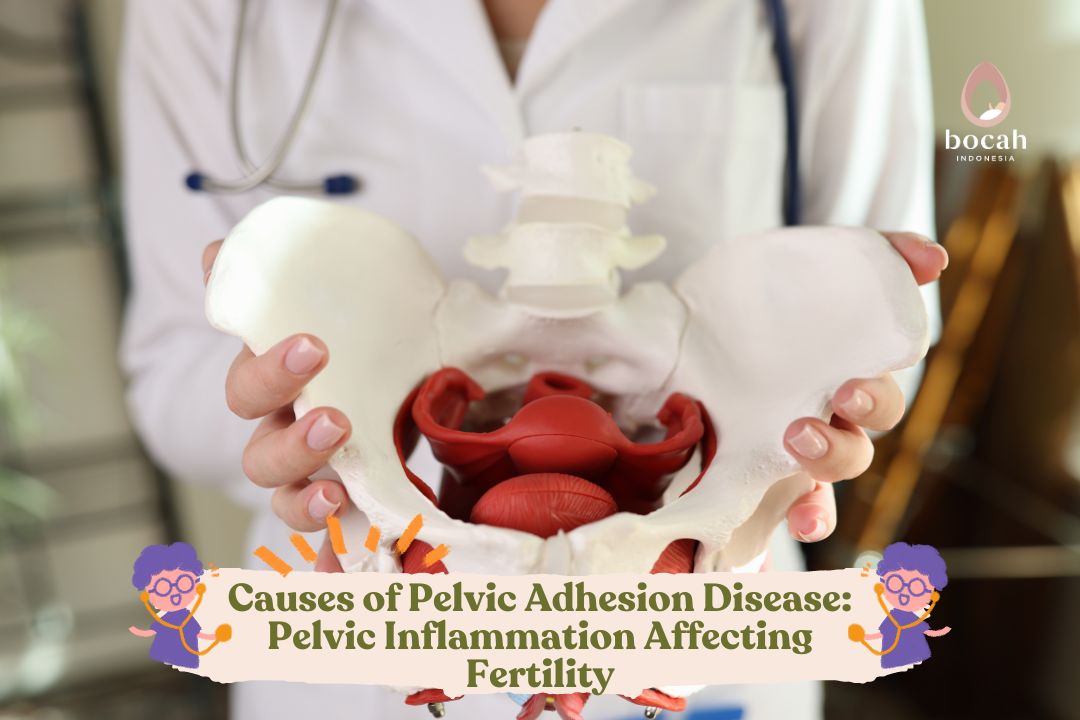
Oophoritis, When the Ovaries Experience Chronic Inflammation
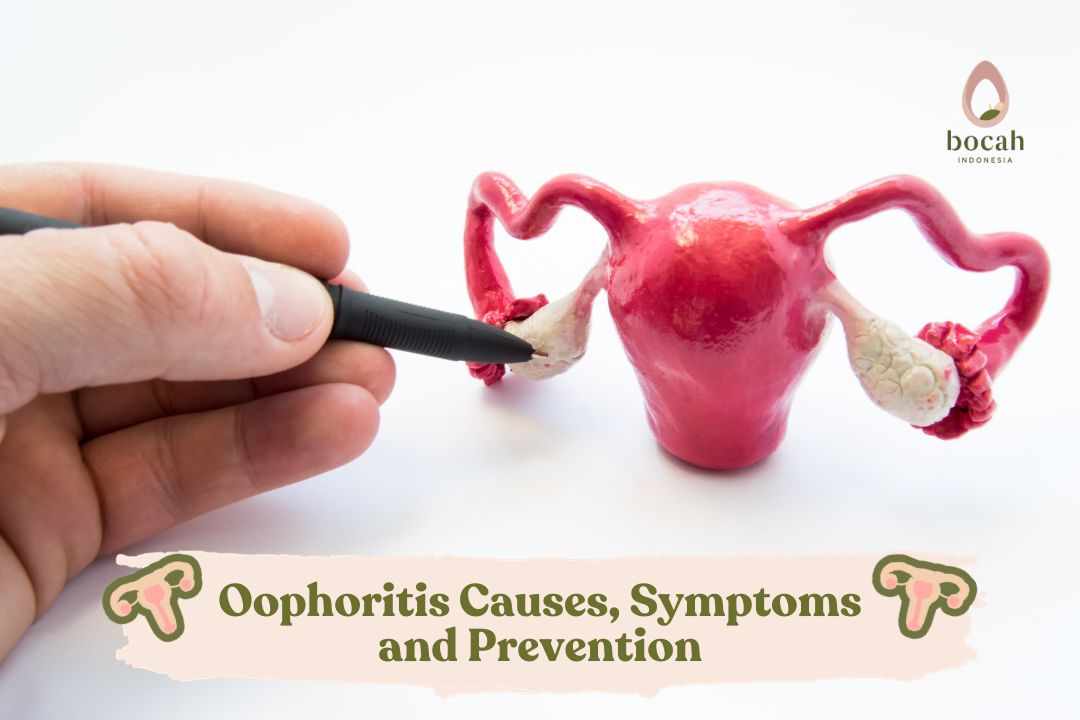
Oophoritis is an infection or inflammation of the ovaries that can affect a woman’s fertility.
The term oophoritis may sound unfamiliar. Oophoritis, or ovaritis, is an inflammatory infection that occurs in the ovaries. Ovarian inflammation is a rare condition that can affect women of any age.
Similar to other types of inflammation, oophoritis can develop into acute or chronic conditions. Chronic inflammation can become a serious condition and may even lead to the loss of reproductive organ function.
Causes of Oophoritis
It’s important to note that oophoritis or ovaritis can be caused by the development of chronic pelvic inflammatory disease or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). However, this condition can also be caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea.
This is because ovarian inflammation occurs due to transmission. The causes are opportunistic microflora bacteria such as staphylococcus, E. coli, streptococcus, mycoplasma, and others. Pathogenic bacteria such as chlamydia, spirochetes, and others.
Tanya Mincah tentang Promil?
Ovarian inflammation generally occurs when the fallopian tubes become infected. This is because the fallopian tubes are the tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. In addition, ovarian inflammation can also occur if the affected person experiences hormonal dysfunction, immune disorders, or a history of gynecological diseases.
There are several risk factors that make women more vulnerable to this condition, such as:
-
During childbirth
-
After a miscarriage
-
When the intrauterine device (IUD) is not inserted correctly
Symptoms of Oophoritis
Generally, oophoritis does not cause any symptoms. If there are symptoms, they are usually mild and difficult to detect. Therefore, special attention is needed for women experiencing some symptoms, such as:
-
Severe vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor
-
Heavier menstrual bleeding than usual
-
Lower abdominal pain
-
Bleeding between menstrual cycles
-
Pain during sexual intercourse
-
Burning or painful sensation during urination
In severe cases, the symptoms can escalate to include:
-
Chills and fever
-
Vomiting
Chronic inflammation can lead to increased genital secretions, which can cause hydrosalpinx and fallopian tube obstruction, preventing sperm from meeting the egg.
Damaged ovaries can lead to menstrual disturbances and ovulation difficulties, causing fertility problems or fertility disorders as well.
How Is Oophoritis Diagnosed?
Considering that the symptoms of ovaritis or ovarian inflammation are quite common and difficult to detect, a diagnosis can be made when specific complaints are experienced by the patient. If this condition occurs, laboratory tests and ultrasound (USG) can be used to determine the extent of inflammation and its level of spread.
Here are some tests that can be performed, including:
-
Blood and urine tests. These tests are performed to determine the white blood cell count to look for signs of inflammation.
-
Pelvic exams. These exams are conducted to detect any abnormalities or symptoms of pelvic inflammation or PID.
-
Transvaginal ultrasonography. A transvaginal ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the ovaries and surrounding areas.
How to Prevent Oophoritis?
Given that this condition is generally caused by the transmission of viruses or bacteria, one way to prevent it is by adopting a healthier lifestyle. Maintaining the hygiene of intimate organs is essential to prevent the entry of viruses or bacteria that can cause ovarian infections or inflammation.
Avoid having sexual intercourse with multiple partners. Try to keep the intimate area dry by wearing comfortable and sweat-absorbing underwear.
So, that’s the explanation about oophoritis or ovaritis. This condition can cause fertility problems and may interfere with your pregnancy plans. If you experience the symptoms mentioned above, it’s best to consult a doctor right away.
Let’s share this information with other women so they can be aware of their condition early on!
Source:
- Ogale, Y., et al. (2018). Self-collection of samples as an additional approach to deliver testing services for sexually transmitted infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Glob Health 2019;4:e001349.
- Jennings, L.K., et al. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.