Understanding the Morulation Process in Embryogenesis
The morulation process is a critical stage in embryogenesis, and various factors can influence its success.
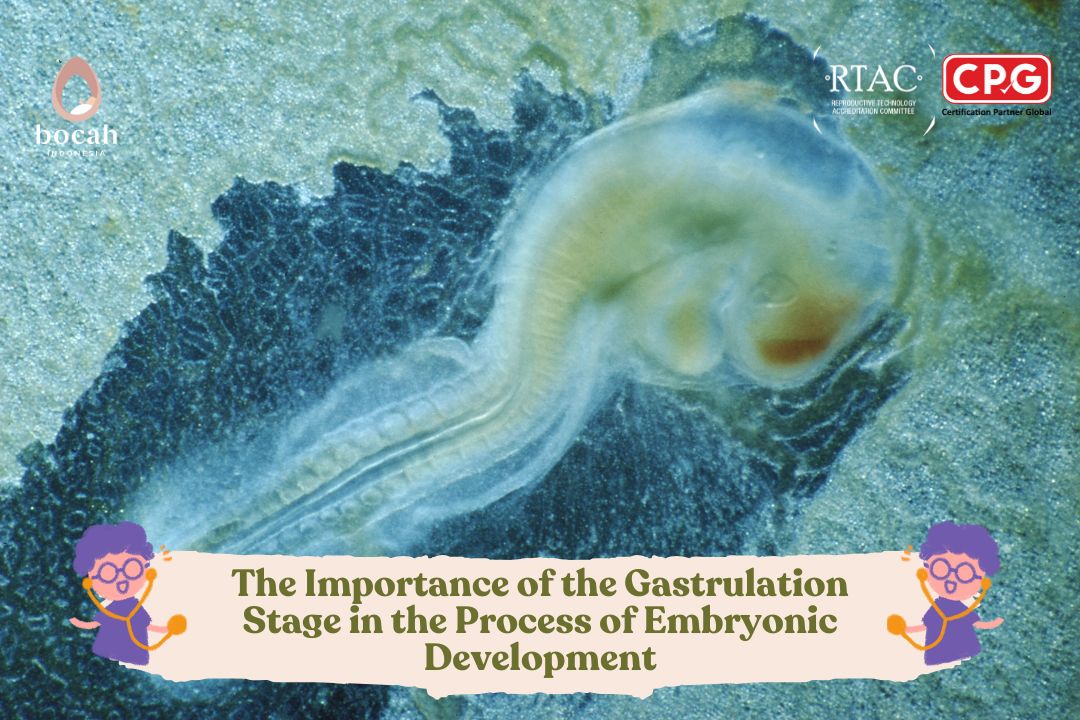
Morulation is one of the early and crucial stages in embryogenesis, the process of developing an embryo from a single cell (zygote) into a complex organism.
At this stage, the zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions, forming a solid structure called the morula. Let’s explore what can disrupt the morulation process and affect embryo development.
Read also: Embryo Growth in IVF Programs
What is Morulation?
Morulation is the process in which a fertilized zygote undergoes repeated mitotic divisions to form a morula. A morula is a solid ball consisting of 16-32 blastomeres tightly bound together.
Mulai Journey of Hope
Stages of Morulation
1. First cleavage division
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes its first cell division through mitosis. The zygote divides into two cells known as blastomeres.
2. Continuous cleavage
Blastomeres continue to divide exponentially, from two to four, eight, and so on. Each division occurs without an increase in total volume, resulting in progressively smaller cells.
3. Morula composition
After several rounds of cell division, the embryo reaches the morula stage, typically on day 3 or 4 after fertilization. The morula consists of approximately 16-32 blastomeres closely packed together, forming a solid structure.
4. Compaction
Cells in the morula undergo a process called compaction, where they move closer together and increase cell-to-cell contact. This compaction is essential for forming a more complex structure in the next stage, the blastula.
Factors That Can Disrupt the Morulation Process
Morulation is an early and crucial stage in embryo development. However, several factors can interfere with this process, leading to embryonic development issues. Below are key factors that can affect morulation:
1. Egg and Sperm Quality and Health
- Genetic mutations: Genetic abnormalities in the egg or sperm can cause critical issues during cell division in morulation.
- DNA damage: Damaged DNA in sperm or eggs can lead to developmental problems from the start.
2. Internal Uterine Environment
- Hormonal imbalances: Unbalanced hormone levels can affect the uterine environment and disrupt embryo development.
- Medical conditions: Conditions such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids can interfere with implantation and embryo development.
3. External Factors
- Toxin exposure: Exposure to toxic chemicals, pesticides, or environmental pollutants can damage eggs or developing embryos.
- Medications: Certain drugs can affect fertility and embryo development if taken during conception and early pregnancy.
4. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Process
- Culture media quality: The culture media used in IVF must support embryo development; otherwise, morulation may be disrupted.
- Laboratory techniques: The techniques used by laboratory technicians in handling embryos must be precise to ensure an optimal environment for development.
5. Stress and Lifestyle
- Physical or emotional stress: High stress levels in expectant mothers can affect hormone levels and egg quality.
- Unhealthy habits: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet can impact reproductive health and embryo development.
6. Genetic Factors
- Chromosomal abnormalities: Chromosomal anomalies such as trisomy or monosomy can cause serious cell division issues during morulation.
- Genetic metabolic disorders: Certain genetic metabolic disorders can hinder normal embryo development.
7. Age
- Women over 35 have a higher risk of experiencing issues with egg quality, which can affect morulation and embryo development.
8. Infections
- Bacterial or viral infections: Certain infections can impact the quality of eggs and sperm, as well as the uterine environment, potentially disrupting morulation.
The Role of Morulation in Embryogenesis
Morulation is a crucial step in embryo development because it:
- Forms the foundation: The morula serves as the foundation from which the blastula and later the gastrula will develop.
- Ensures cell distribution: The cell divisions during morulation ensure the genetic material is evenly distributed among all blastomeres.
- Prepares for implantation: This stage prepares the embryo for implantation in the uterine wall, which will occur after the morula develops into the blastula and then the blastocyst.
Morula vs. Blastula
After the morula stage, the embryo enters the blastulation phase, where the morula develops into a blastula. The main differences between morula and blastula are:
- Morula: A dense cluster of blastomere cells.
- Blastula: A structure with a fluid-filled cavity (blastocoel) in the center, formed through a process called blastulation.
Conclusion
Morulation is an essential early stage in embryogenesis, preparing the embryo for further development.
Through a series of organized cell divisions and compaction, the zygote develops into a morula, laying the groundwork for more complex structures such as the blastula and, eventually, a fully developed organism.
For more information on fertility, reproductive health, or pregnancy programs, visit the Bocah Indonesia website.
Source:
- Browne W.E. et al. (2005). Stages of Embryonic Development in the Amphipod Crustacean, Parhyale hawaiensis.
- Hall T.E. et al. (2004). Stages of Embryonic Development in the Atlantic Cod Gadus morula.
- Kimmel C.B. et al. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish.
- Cherry, Kendra, MSEd.(2023). Very Well. Stages of Prenatal Development
- Mittelmark, Raul Artal (2022). MSD Manual. Physical Changes During Pregnancy
- Fasting While Trying to Conceive? Healthy Meal Ideas for the Entire Month - 04/03/2026
- 12 Foods to Help You Get Pregnant Faster - 03/03/2026
- 3 Juice Recipes for a Pregnancy Program - 26/02/2026